How to properly use interactive display teaching in the classroom?
In the past two or three years, due to the adjustment of the company’s business direction, we have cooperated with several well-known preschool education groups to develop a large number of courseware used in classroom collective teaching scenarios, accumulating thousands of different types of interactive displays(interactive screens).
Many say that because they are not dealing with “users” but “customers,” developing B-side products is much less fulfilling than developing C-side products, and they always feel incomplete. Fortunately, when we developed B-side products, we got the support of our partners and contacted a large number of users.
It is precise because we can truly see the feedback of each user (children and teachers) after doing thousands of classroom interaction displays we summarize these experiences and tell you How to properly use interactive display teaching in the classroom?
Application scenarios of Interactive Display
Let’s first describe the approximate application scenario of the interactive displays: in a classroom of about 30 square meters, a teacher is standing next to the interactive TV. The height of the TV is similar to the height of the teacher’s raised arms, about 3 meters away Distance, 25 children sit on chairs in a semicircle (many numbers appearing here will affect the interaction design of the product).
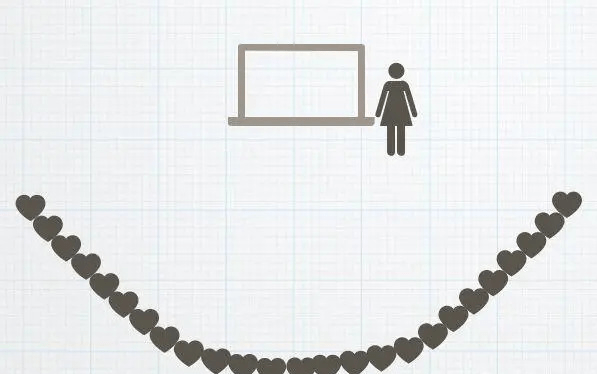
When switching from the C-end to the B-end, we simply cannot imagine that the height of the child and the height of the display need to be considered in product design.
When we took the first batch of developed games to the kindergarten for a trial class, there was such a scene: for the child to reach the operation objects on display, the teacher had to pick up the child; some teachers simply refused to let the child save trouble. Do it yourself, but ask the child to stand under the TV and signal with their hands…
Although each kindergarten’s interactive display height and screen size are different, a good product needs to be as convenient as possible for the actual users. ” other factors are added to enhance the product experience.
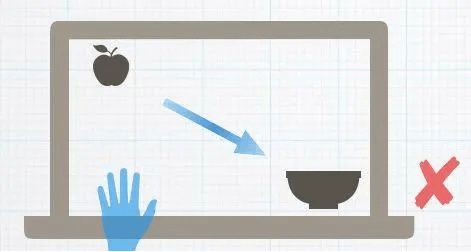
When designing, keep actionable objects in the lower middle of the screen as much as possible, especially for younger children. At the same time, because young children are not mature enough to control their hand muscles, long-distance and continuous dragging are very difficult. Therefore, it is necessary to minimize the increase in the game’s difficulty due to the limitation of the physiological development level.
For example, dragging an apple from the upper left corner to the lower right corner of the display can cause incredible frustration for children.
What if the child’s attention is drawn to other content on the screen?
We all know that children have short attention spans and are easily attracted to novel stimuli. During the trial class, we found that some elements, dynamic effects, etc., originally intended to increase the fun of the product or create small surprises, have instead become the “culprit” that hinders the teacher’s smooth control of the normal classroom rhythm.
For example, after a child completes an operation task correctly, dynamic feedback is immediately given on the screen. Still, because the input is more vivid, all the children move along with it. You can imagine a group of “active” as The natural 3-6-year-olds, after encountering a “Ran Dian,” how lively the whole class is! !!
Although for this kind of “overwhelming” interaction, the team members didn’t all agree that it needed to be changed at first. To let everyone truly feel the difference between the group teaching scene and the C-side independent game scene, we let everyone involved in the development go to the classroom to follow the class on the spot. After everyone had an intuitive feeling, we explained the right Children to speak different behavioral paths in the two scenarios.
For example, in the picture below, the main body of the game is the pool in the middle and the people swimming. But to increase the interest, the designer added a fluttering red balloon in the upper left corner of the interactive display so that children can explore by themselves. When the balloon is clicked, the balloon can fly, can be broken, and so on.
In this game, for C-end-oriented products (take mobile phones as an example), the child’s behavior path is visual focus – action focus, that is, the child sees the shaking balloon. Then this curiosity will drive them To make the action of clicking the balloon and then getting the corresponding feedback.
And once this interaction becomes a group teaching scene, the behavioral path becomes: visual focus-expression-(action); the shaking balloon will still attract the child’s attention, but because of the limitation of the scene, they cannot achieve immediate turning Action focus, then it becomes the way to achieve – “speak,” they will ask all kinds of questions.
Of course, we also advocate the protection and encouragement of children’s curiosity and the various problems that arise from it. Still, teachers must have a higher “field control ability,” and at the same time, they also propose challenges to achieve teaching goals.

What if my child is not interested in using interactive screens to learn?
When we designed and developed the interaction of this courseware, we had an idea at the beginning: use different things to stimulate children’s continuous interest. Therefore, as much as possible, more than one material will be provided in the game.
For example, when understanding addition, we use fruits and numbers to establish a corresponding relationship, so three kinds of fruits are provided, and the system randomly appears with one. As a result, during class, the following scene appeared:
Teacher: “Let’s see what fruit is?”
Child: “Why is it a strawberry again, teacher? Let’s change it to a banana!”
It was originally a good starting point, but after careful analysis, you will find that there is a self-defeating place: children and teachers have no expectations for the content of the courseware itself, and we let them have an expectation randomly, that is, “the fruit will be different each time it appears.”
When the child has inertia, once the expectations fail again and again, it is easy to be disappointed or even angry.
Therefore, we must first focus on the core goal of teaching and then consider adding “openness” or “randomness” and whether it is a burden or a convenience for the cognition of teachers and children. In what way of presentation and selection more appropriate and so on?

How do we let more children learn from the interactive screen educational model?
The last thing I want to share is that when the kindergarten first started using the courseware, the principal and the teacher worried the most: how to take care of more children?
Whether from the achievement of teaching effect or the development of home co-education, it is necessary to allow every child to participate in every class as much as possible. But, in the limited group teaching time, every child can’t experience every game on the screen. How to do it?
After continuous attempts, we finally returned to the essence of “educational games” to optimize the interactive design of the game. It is using a form of gamification to make collective activities better achieve their goals; that is to say, the problem to be solved is: whether children who operate on the screen or children who do not operate on the screen can participate in the game, can reach the target.
Therefore, when designing the game, you can add more tasks that require cooperation to complete the game goal; in the process of a child’s operation, try to provide interactions that allow other children to participate as much as possible, such as voice guidance, etc.

To a certain extent, the interaction design of the B-end is compared with the C-end products because the application scenarios are more complex and more people participate. It will be more difficult to achieve a good interactive experience.
Therefore, to bring the best interactive display experience to customers, ValueTek constantly updates hardware and software technologies, which is why we can become one of the best interactive display manufacturers in China.